Beyond serving as a tool for communicating emotional experiences, can language also support emotion understanding and inference? To explore this question, Zhang Dan's research group from the Department of Psychology and Cognitive Science at Tsinghua University, in collaboration with Liu Zhiyuan's research group from the Department of Computer Science and Technology, used large language models (LLMs) to investigate the representational characteristics of emotion knowledge acquired through language experience. Their study revealed a causal connection between emotion knowledge representations based on language experience and emotion inference abilities.
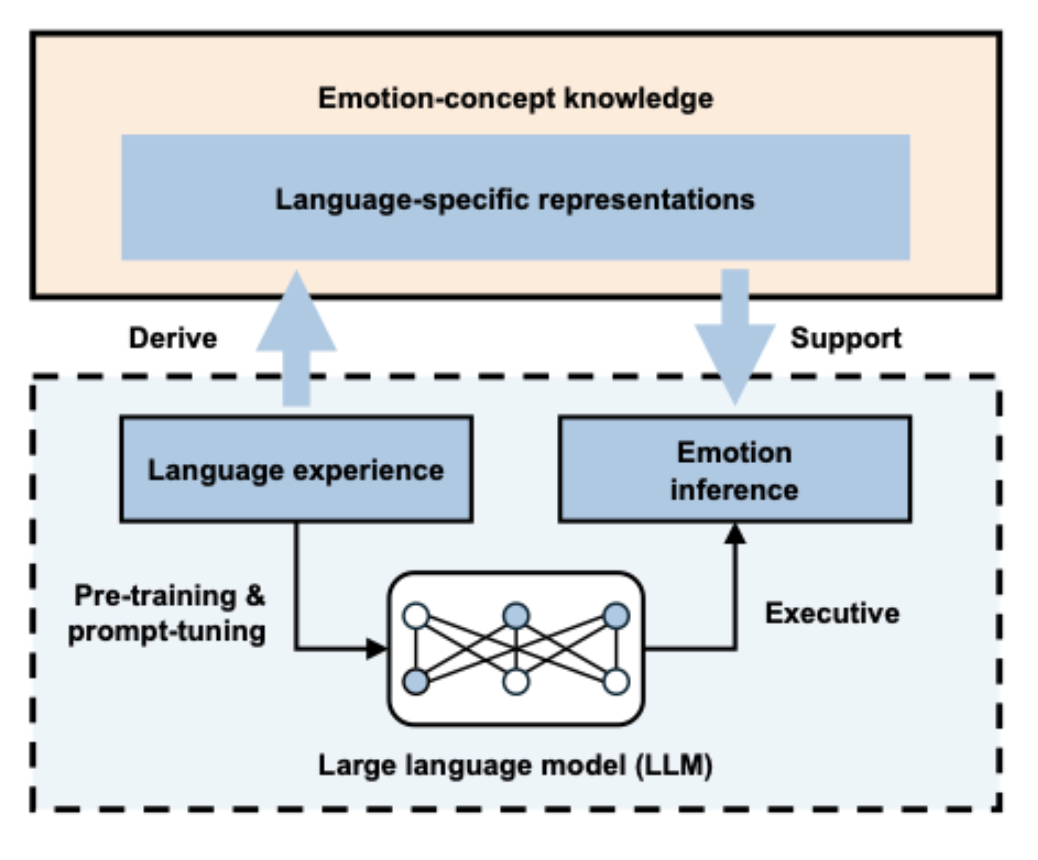
Figure 1: Research Framework
This research used LLMs as models with only language experience but lacking sensory-motor experience to study how language itself represents emotional concept knowledge. The study found that 14 major attributes of human emotion concepts (based on independent behavioral experiments) are represented by different artificial neuron populations in LLMs. By manipulating these neurons associated with emotion concept attributes, the researchers further confirmed the role of emotion concept knowledge in generative emotion inference: the degree of performance decline in LLMs on emotion inference tasks correlated with the importance of different attributes in human psychological space.
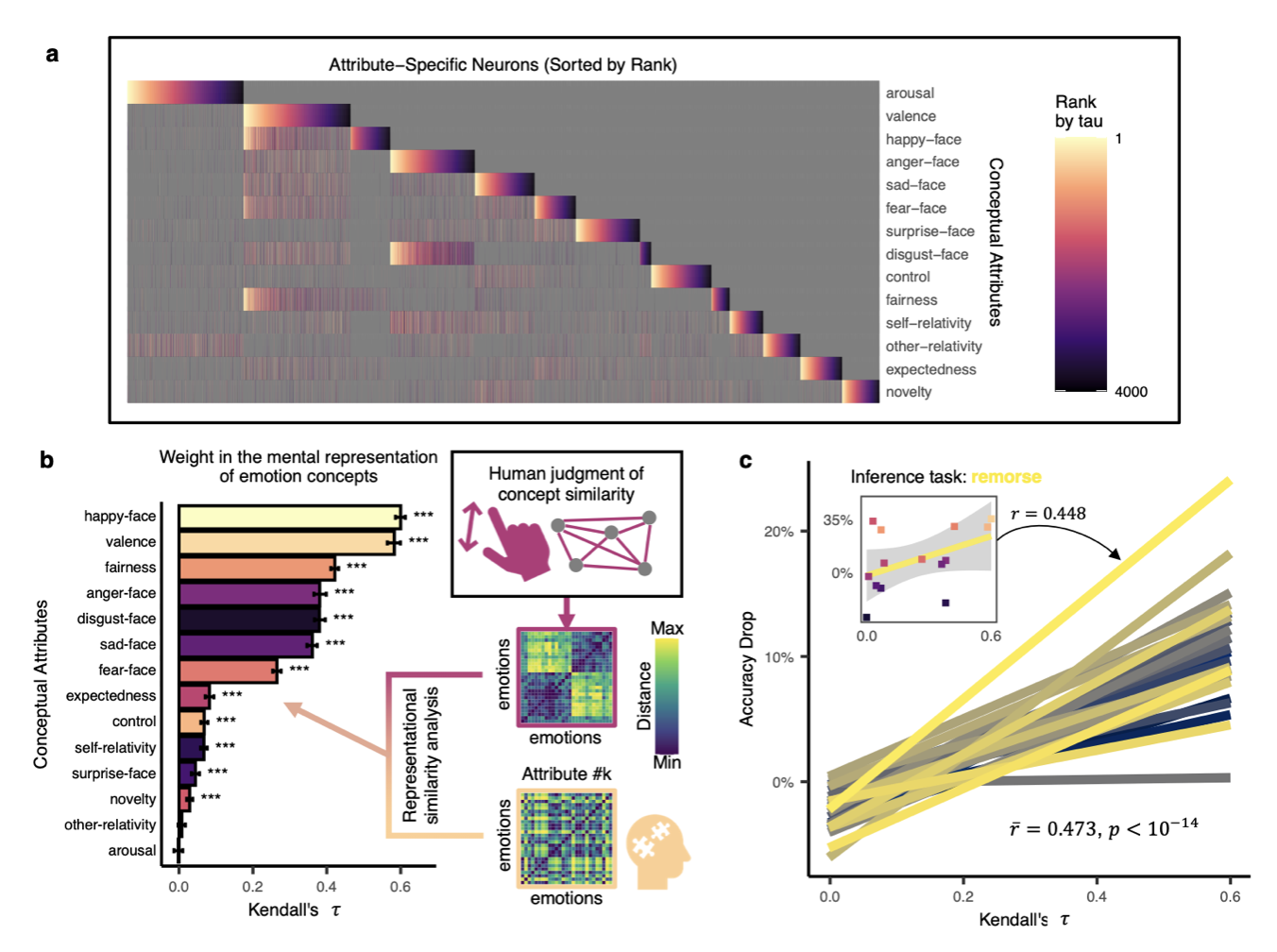
Figure 2: Main Research Results. a) Distribution of neurons specific to 14 human emotion concept attributes in LLMs; b) Importance of different emotion concept attributes in human psychological space; c) The more important an emotion concept attribute is in human psychological space, the worse the LLM's emotion inference ability becomes after manipulating its specific neurons.
The findings provide crucial evidence from the perspective of large language models for the important role of language in human emotion understanding. The results suggest that even artificial intelligence without any sensory-motor experience can learn and reason about emotions with the support of language. The study offers a new perspective on the debate about the "essence" of human emotions and provides valuable insights for developing socially and emotionally intelligent artificial intelligence in the future.
This research has been officially accepted and published online in iScience, a journal under Cell Press. Ming Li, a doctoral student from the Department of Psychology and Cognitive Science at Tsinghua University, and Yusheng Su, a graduated doctoral student from the Department of Computer Science and Technology, are co-first authors of this paper. Associate Professor Zhang Dan from the Department of Psychology and Cognitive Science and Associate Professor Liu Zhiyuan from the Department of Computer Science and Technology are co-corresponding authors.
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (T2341003, 62236004), the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2020AAA0106500), the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the German Research Foundation's Cross-Modal Learning Project (NSFC 62061136001/DFG TRR-169/C1, C4), the Teaching Reform and Research Project of the Psychology Teaching Guidance Committee of Higher Education Institutions of the Ministry of Education (20222008), and the Undergraduate Teaching Reform Project of Tsinghua University (DX05_02).
Paper Information: Li, M.#, Su, Y.#, Huang, H.-Y., Cheng, J., Hu, X., Zhang, X., Wang, H., Qin, Y., Wang, X., Lindquist, K.A., Liu, Z., Zhang, D. (2024). Language-Specific Representation of Emotion-Concept Knowledge Causally Supports Emotion Inference. iScience, 111401.
Paper Link: https://www.cell.com/iscience/fulltext/S2589-0042(24)02626-9

